Congratulations to Xia and Chun for their recently accepted paper in JGR-Biogeosciences.
Significant Inconsistency of Vegetation Carbon Density in CMIP5 Earth System Models against Observational Data
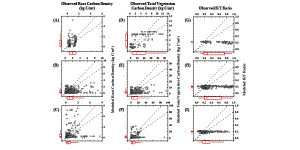
Earth System Models (ESMs) have been widely used for projecting global vegetation carbon dynamics, yet how well ESMs performed for simulating vegetation carbon density remains untested. We compiled observational data of vegetation carbon density from literature and existing datasets to evaluate nine ESMs at site, biome, latitude and global scales. Three variables – root (including fine and coarse roots), total vegetation carbon density, and the root: total vegetation carbon ratios (R/T ratios), were chosen for ESM evaluation. ESM models performed well in simulating the spatial distribution of carbon densities in root (r = 0.71) and total vegetation (r = 0.62). However, ESM models had significant biases in simulating absolute carbon densities in root and total vegetation biomass across the majority of land ecosystems, especially in tropical and arctic ecosystems. Particularly, ESMs significantly overestimated carbon density in root (183%) and total vegetation biomass (167%) in climate zones of 10S ~ 10N. Substantial discrepancies between modeled and observed R/T ratios were found: the R/T ratios from ESMs were relatively constant, approximately 0.2 across all ecosystems, along latitudinal gradients, and in tropic, temperate, and arctic climatic zones, which was significantly different from the observed large variations in the R/T ratios (0.1 ~ 0.8). There were substantial inconsistencies between ESMs derived carbon density in root and total vegetation biomass and the R/T ratio at multiple scales, indicating urgent needs for model improvements on carbon allocation algorithms and more intensive field campaigns targeting carbon density in all key vegetation components.
http://agupubs.onlinelibrary.wiley.com/hub/article/10.1002/2017JG003914/editor-highlight/